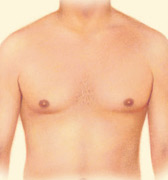
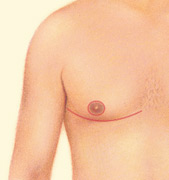
.jpg) Gynecomastia, a condition of over-developed or enlarged breasts in men, is common in men of any age. It can be the result of hormonal changes, heredity conditions, disease or the use of certain drugs.
Gynecomastia, a condition of over-developed or enlarged breasts in men, is common in men of any age. It can be the result of hormonal changes, heredity conditions, disease or the use of certain drugs.
With the procedure on the rise, more than 22,939 people had gynecomastia surgery in 2013. The condition can be the result of hormonal changes, heredity, obesity, or the use of certain drugs. Gynecomastia can cause emotional discomfort and impair your self confidence. Some men may even avoid certain physical activities and intimacy simply to hide their condition.
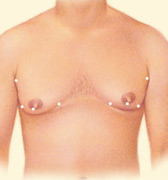
Plastic surgery to correct gynecomastia is technically called reduction mammaplasty. The procedure reduces breast size, flattening and enhancing the chest contours. In severe cases of gynecomastia, the weight of excess breast tissue may cause the breasts to sag and stretch the areola (the dark skin surrounding the nipple). In these cases the position and size of the areola can be surgically improved and excess skin may be reduced.
Gynecomastia is characterized by:
- Excess localized fat
- Excess glandular tissue development
- A combination of both excess fat and glandular tissue
- Gynecomastia may be present unilaterally (one breast) or bilaterally (both breasts)
Is it right for me?
Gynecomastia surgery is a highly individualized procedure and you should do it for yourself, not to fulfill someone else’s desires or to try to fit any sort of ideal image.
This procedure is a good option for you if:
- You are physically healthy and of relatively normal weight
- You have realistic expectations
- Your breast development has stabilized
- You are bothered by the feeling that your breasts are too large
Adolescents may benefit from surgery, although secondary procedures may be needed in the future should breast development continue.
Surgical correction of gynecomastia is best performed on:
- Men whose condition cannot be corrected through alternative medical treatments
- Healthy individuals who do not have a life-threatening illness or medical conditions that can impair healing
- Non-smokers and non-drug users
- Men with a positive outlook and specific goals
- In mind for improving the physical symptoms of gynecomastia
The success and safety of your gynecomastia procedure depends very much on your complete candidness during your consultation. You’ll be asked a number of questions about your health, desires and lifestyle.
.jpg)
Be prepared to discuss:
- Why you want the surgery, your expectations and desired outcome
- Medical conditions, drug allergies and medical treatments
- Use of current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco and drugs including steroids
- Previous surgeries
Your surgeon may also:
- Evaluate your general health status and any pre-existing health conditions or risk factors
- Perform diagnostic testing to determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia; this may include testing of your endocrine function
- Examine your breasts and may take detailed measurements of their size and shape, skin quality, and placement of your nipples and areolas
- Take photographs for your medical records
- Discuss your options
- Recommend a course of treatment
- Discuss likely outcomes of gynecomastia
- Correction and any risks or potential complications
- Discuss the use of anesthesia during your procedure
.jpg) Prior to surgery, you may be asked to:
Prior to surgery, you may be asked to:
- Get lab testing or a medical evaluation
- Take certain medications or adjust your current medications
- Stop smoking well in advance of surgery
- Avoid taking aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs and herbal supplements as they can increase bleeding
The success and safety of your gynecomastia procedure depends very much on your complete candidness during your consultation. You’ll be asked a number of questions about your health, desires, and lifestyle. Breast reduction surgery may be performed in an accredited, office-based surgical facility, licensed ambulatory surgical center, or a hospital. Be sure to arrange for someone to drive you to and from surgery and to stay with you for at least the first night following surgery.
What happens during gynecomastia correction surgery?
Plastic surgery to correct gynecomastia is technically called reduction mammaplasty, and reduces breast size, flattening and enhancing the chest contours.
In severe cases of gynecomastia, the weight of excess breast tissue may cause the breasts to sag and stretch the areola (the dark skin surrounding the nipple). In these cases the position and size of the areola can be surgically improved and excess skin may be reduced.
Anesthesia
Medications are administered for your comfort during the surgical procedures. The options include intravenous sedation and general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best option for you.
Liposuction
In cases where gynecomastia is primarily the result of excess fatty tissue, liposuction techniques alone may be used. This requires insertion of a cannula, a thin hollow tube, through several small incisions. The cannula is moved back and forth in a controlled motion to loosen the excess fat, which is then removed from the body by vacuum suction. There are various liposuction techniques that may be used; the technique most appropriate in your case will be defined prior to your procedure.
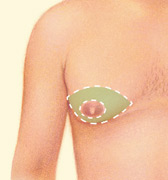
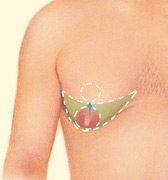
Excision
Excision techniques are recommended where glandular breast tissue or excess skin must be removed to correct gynecomastia. Excision also is necessary if the areola will be reduced or the nipple will be repositioned to a more natural male contour. Incision patterns vary depending on the specific conditions and surgical preference.
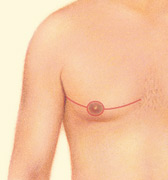
Sometimes gynecomastia is treated with both liposuction and excision.
Will there be scars?
Any surgical treatment to correct gynecomastia will require incisions. While most incision lines are concealed within natural contours, some may be visible and are a necessary result of breast reduction surgery.
The decision to have gynecomastia surgery is extremely personal, and you’ll have to decide if the benefits will achieve your goals and if the risks and potential complications are acceptable. You will be asked to sign consent forms to ensure that you ully understand the procedure and any risks and potential complications.
The risks include:
- Reactions to tape, suture materials, glues, topical preparations, or injected agents
- Anesthesia risks
- Bleeding (hematoma)
- Blood clots
- Breast asymmetry
- Breast contour and shape irregularities
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation may be temporary or permanent
- Damage to deeper structures – such as nerves, blood vessels, muscles, and lungs – can occur and may be temporary or permanent
- Deep vein thrombosis, cardiac and pulmonary complications
- Fatty tissue found in the breast might die (fat necrosis)
- Fluid accumulation (seroma)
- Infection
- Persistent pain
- Poor wound healing
- Possibility of revisional surgery
- Unfavorable scarring
Where will my surgery be performed?
Surgery to correct gynecomastia may be performed on an outpatient basis, in an office-based or ambulatory surgical facility, or a hospital setting. It may be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
These decisions will be based on the requirements of your specific procedure and in consideration of your preference and your doctor’s best judgment. Your plastic surgeon and the assisting staff will fully attend to your comfort and safety.
When you go home
If you experience shortness of breath, chest pains, or unusual heart beats, seek medical attention immediately. Should any of these complications occur, you may require hospitalization and additional treatment.
Be careful
Following your physician’s instructions is key to the success of your surgery. It is important that the surgical incisions are not subjected to excessive force, abrasion, or motion during the time of healing. Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to care for yourself.
Be sure to ask questions: It’s important that you address all your questions directly with your plastic surgeon. It’s natural to feel some anxiety, whether excitement for the anticipated outcomes or preoperative stress. Discuss these feelings with your plastic surgeon.
After surgery, dressings or bandages will be applied to your incisions and an elastic bandage or support garment may be used to minimize swelling and support your new chest contour as it heals.
A small, thin tube may be temporarily placed under the skin to drain any excess blood or fluid that may collect.
.jpg) You will be given specific instructions that may include: How to care for your surgical site(s) following surgery, medications to apply or take orally to aid healing and reduce the risk of infection, specific concerns to look for at the surgical site or in your general health, and when to follow up with your plastic surgeon.
You will be given specific instructions that may include: How to care for your surgical site(s) following surgery, medications to apply or take orally to aid healing and reduce the risk of infection, specific concerns to look for at the surgical site or in your general health, and when to follow up with your plastic surgeon.
Be sure to ask your plastic surgeon specific questions about what you can expect during your individual recovery period.
- Where will I be taken after my surgery is complete?
- What medication will I be given or prescribed after surgery?
- Will I have dressings/bandages after surgery? When will they be removed?
- Are stitches removed? When?
- When can I resume normal activity and exercise?
- When do I return for follow-up care?
It’s very important to follow your plastic surgeon’s instructions and attend follow-up visits as scheduled.
.jpg) The final results of the breast reduction procedure are permanent in many cases. However, if gynecomastia resulted from the use of certain prescription medications, drugs (including steroids), or weight gain you must be fully free from these substances and remain at a stable weight in order to maintain your results. Please discuss this with your physician before making changes to your prescription medications.
The final results of the breast reduction procedure are permanent in many cases. However, if gynecomastia resulted from the use of certain prescription medications, drugs (including steroids), or weight gain you must be fully free from these substances and remain at a stable weight in order to maintain your results. Please discuss this with your physician before making changes to your prescription medications.
Any surgical treatment to correct gynecomastia will require incisions. While most incision lines are concealed within natural contours, some may be
visible and are a necessary result of breast reduction surgery. All scars are permanent, even though some scars may be concealed in the natural contours of the breast. Your improved upper body will likely enhance your self-image and confidence, whether in a shirt and tie, a t-shirt, or baring your chest at the beach.
Cost is always a consideration in elective surgery. Prices for gynecomastia can vary widely. A surgeon’s cost for gynecomastia may vary based on his or her experience as well as geographic location.
Many plastic surgeons offer patient financing plans, so be sure to ask.
Cost may include:
- Surgeon’s fee
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- Anesthesia fees
- Prescriptions for medication
- Post-surgery garments, and
- Medical tests
In most cases, correction of gynecomastia is not eligible for insurance coverage. However, each insurance policy varies greatly. Carefully review your policy to determine coverage. The American Society of Plastic Surgeons has published a position paper for physicians and insurers defining the recommended criteria for reconstructive cases of gynecomastia. Ask your physician for a copy of this document to submit to your insurer.
.jpg) Your satisfaction involves more than a fee
Your satisfaction involves more than a fee
When choosing a plastic surgeon for gynecomastia surgery, remember that the surgeon’s experience and your comfort with him or her are just as important as the final cost of the surgery.
- Areola: Pigmented skin surrounding the nipple.
- Bilateral gynecomastia: A condition of over-developed or enlarged breasts in men affecting both breasts.
- Endocrine system: A group of glands that make hormones which help to control activities in your body such as reproduction, metabolism, growth and development. Testing of your endocrine system may be done to look for signs of diabetes, thyroid disorders, growth hormone deficiency, osteoporosis, hypertension and obesity.
- Excision: To remove the skin.
- General anesthesia: Drugs and/or gases used during an operation to relieve pain and alter consciousness.
- Hematoma: Blood pooling beneath the skin.
- Intravenous sedation: Sedatives administered by injection into a vein to help you relax.
- Liposuction: Also called lipoplasty or suction lipectomy, this procedure vacuums out fat from beneath the skin’s surface to reduce fullness.
- Local anesthesia: A drug injected directly to the site of an incision during an operation to relieve pain.
- Reduction mammaplasty: The surgical removal of breast tissue to reduce the size of breasts.
- Sutures: Stitches used by surgeons to hold skin and tissue together.
- Unilateral gynecomastia: A condition of over-developed or enlarged breasts in men affecting just one breast.
Use this checklist as a guide during your consultation
- Are you certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery?
- Were you trained specifically in the field of plastic surgery?
- How many years of plastic surgery training have you had?
- Do you have hospital privileges to perform this procedure?
- If so, at which hospitals?
- Is the office-based surgical facility accredited by a nationally- or state-recognized accrediting agency, or is it state-licensed or Medicare-certified?
- Am I a good candidate for this procedure?
- What will be expected of me to get the best results?
- Where and how will you perform my procedure?
- What surgical technique is recommended for me?
- How long of a recovery period can I expect, and what kind of help will I need during my recovery?
- What are the risks and complications associated with my procedure?
- How are complications handled?
- What are my options if I am dissatisfied with the outcome of my surgery?
- Do you have before-and-after photos I can look at for this procedure and what results are reasonable for me?
Plastic surgery involves many choices. The first and most important is selecting a surgeon you can trust.
Choosing an ASPS Member Surgeon ensures that you have selected a physician who:
- Has completed at least five years of surgical training with a minimum of two years in plastic surgery.
- Is trained and experienced in all plastic surgery procedures, including breast, body, face and reconstruction.
- Operates only in accredited medical facilities
- Adheres to a strict code of ethics.
- Fulfills continuing medical education requirements, including standards and innovations in patient safety.
- Is board certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or in Canada by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada®.
ASPS Member Surgeons are your partners in cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery.
Look for the ASPS Member Surgeon logo.

 3510 N. Ridge Rd, Suite 100
3510 N. Ridge Rd, Suite 100