 Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation surgery involves using breast implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts (breast enlargement) or to restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy (breast enhancement).
Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation surgery involves using breast implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts (breast enlargement) or to restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy (breast enhancement).
If you are dissatisfied with your breast size, breast augmentation surgery (either breast enhancement or breast enlargement) is a choice to consider. Breast augmentation can:
- Increase fullness and projection of your breasts
- Improve the balance of your figure
- Enhance your self-image and self-confidence
Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, the procedure involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy.
Implants also may be used to reconstruct a breast after mastectomy or injury.
Many patients find it helpful to review breast augmentation before and after photos.
What it won’t do
Breast augmentation does not correct severely drooping breasts. If you want your breasts to look fuller and to be lifted due to sagging, a breast lift may be required in conjunction with breast augmentation.
Breast lifting can often be done at the same time as your augmentation or may require a separate operation. Your plastic surgeon will assist you in making this decision.
Is it right for me?
Breast augmentation is a highly individualized procedure and you should do it for yourself, not to fulfill someone else’s desires or to try to fit any sort of ideal image. Pictures of breast augmentation procedures performed by ASPS Member Surgeons may help you in the decision-making process.
Breast augmentation may be a good option for you if:
- You are physically healthy
- You have realistic expectations
- Your breasts are fully developed
- You are bothered by the feeling that your breasts are too small
- You are dissatisfied with your breasts losing shape and volume after pregnancy, weight loss, or with aging
- Your breasts vary in size or shape
- One or both breasts failed to develop normally
The success and safety of your breast augmentation procedure depends very much on your being completely candid during your consultation. By being actively involved your consultation about breast augmentation, problems, concerns and questions you may have can be addressed by your ASPS Member Surgeon. You’ll be asked a number of questions about your health, desires and lifestyle.
.jpg) Be prepared to discuss:
Be prepared to discuss:
- Why you want breast augmentation surgery, your expectations and desired outcome
- Medical conditions, drug allergies and medical treatments
- Use of current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco and drugs
- Previous surgeries
- Family history of breast cancer and results of any mammograms or previous biopsies
Your surgeon may also:
- Evaluate your general health status and any pre-existing health conditions or risk factors
- Examine your breasts, and may take detailed measurements of their size and shape, skin quality, placement of your nipples
- Take photographs for your medical record
- Discuss your options and recommend a course of treatment
- Discuss likely outcomes of breast augmentation surgery and any risks or potential complications
- Discuss the use of anesthesia during your breast augmentation procedure
.jpg) After researching the basics about breast enhancement or breast enlargement, many patients want to know what to expect before breast augmentation surgery.
After researching the basics about breast enhancement or breast enlargement, many patients want to know what to expect before breast augmentation surgery.
Prior to breast surgery, your ASPS Member Surgeon may ask you to:
- Get lab testing or a medical evaluation
- Take certain medications or adjust your current medications
- Get a baseline mammogram before surgery and another one after surgery to help detect any future changes in your breast tissue
- Stop smoking well in advance of your breast augmentation surgery
- Avoid taking aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs and herbal supplements as they can increase bleeding
Special instructions you receive will cover:
- What to do on the day of surgery
- Post-operative care and follow-up
- Breast implant registry documents (when necessary)
Your plastic surgeon will also discuss where your procedure will be performed. Breast augmentation surgery may be performed in an accredited office-based surgical center, outpatient ambulatory surgical center or a hospital.
You’ll need help
If your breast augmentation is performed on an outpatient basis, be sure to arrange for someone to drive you to and from surgery and to stay with you for at least the first night following surgery.
What happens during breast augmentation surgery?
Step 1 – Anesthesia
Medications are administered for your comfort during breast augmentation surgery. The choices include intravenous sedation and general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best choice for you.
Step 2 – The incision
Incisions are made in inconspicuous areas to minimize visible scarring. You and your plastic surgeon will discuss which incision options are appropriate for your desired outcome. Incision options include:
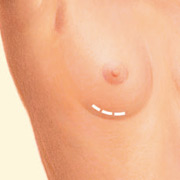
Inframammary incision
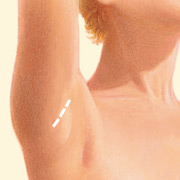
Transaxillary incision
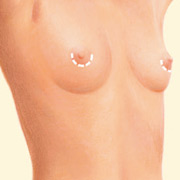
Periareolar incision
Incisions vary based on the type of implant, degree of enlargement desired, your particular anatomy, and patient-surgeon preference.
Step 3 – Implant choice: Silicone breast implants or saline breast implants?
Breast size and shape are important, so be honest and open about your expectations when talking with your surgeon.
Implant type and size will be determined not just on your desired increase in size but more importantly on your breast anatomy, skin elasticity and body type.
Options for Breast Implants
Saline breast implants are filled with sterile salt water. They can be filled with varying amounts of saline which can affect the shape, firmness and feel of the breast. Should the implant shell leak, a saline breast implant will collapse and the saline will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body.
Silicone breast implants are filled with an elastic gel. The gel feels and moves much like natural breast tissue. If the implant leaks, the gel may remain within the implant shell, or may escape into the breast implant pocket.
A leaking implant filled with silicone gel may not collapse. If you choose these implants, you may need to visit your plastic surgeon regularly to make sure the implants are functioning properly. An ultrasound or MRI screening can assess the condition of breast implants.
Implant manufacturers occasionally introduce new styles and types of implants, so there may be additional options available.
Currently Saline breast implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women 18 years of age and older.
Currently Silicone breast implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women 22 years of age and older.
Saline or silicone implants may be recommended at a younger age if used for reconstruction purposes.
See http://www.breastimplantsafety.org/ for current information.
Step 4 – Inserting and placing the breast implant
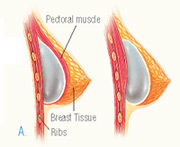 After the incision is made, a breast implant is inserted into a pocket either:
After the incision is made, a breast implant is inserted into a pocket either:
- Under the pectoral muscle (a submuscular placement), or
- Directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle (a submammary/ subglandular placement)
The method for inserting and positioning implants depends on the type of implant, degree of enlargement desired, your body type, and your surgeon’s recommendations.
Step 5 – Closing the incisions
Incisions are closed with layered sutures in the breast tissue and with sutures, skin adhesive or surgical tape to close the skin. Over time the incision lines will fade.

Step 6 – See the results
The results of breast augmentation surgery are immediately visible. Over time, post-surgical swelling will resolve and incision lines will fade. Satisfaction with your new image should continue to grow as you recover and realize the fulfillment of your goal for fuller breasts.
The decision to have breast augmentation surgery is extremely personal and you’ll have to decide if the benefits will achieve your goals and if the risks of breast implant safety and potential complications are acceptable.
Your plastic surgeon and/or staff will explain in detail the risks associated with surgery. You will be asked to sign consent forms to ensure that you fully understand the procedure you will undergo and any risks or potential complications.
The risks of breast implants and complications after breast augmentation include:
- Unfavorable scarring
- Bleeding (hematoma)
- Infection
- Poor healing of incisions
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation, may be temporary or permanent
- Capsular contracture, which is the formation of firm scar tissue around the implant
- Implant leakage or rupture
- Wrinkling of the skin over the implant
- Anesthesia risks
- Fluid accumulation
- Blood clots
- Pain, which may persist
- Deep vein thrombosis, cardiac and pulmonary complications
- Possibility of revisional surgery
Although there potentially may be complications with breast implants, they do not impair breast health. Careful review of scientific research conducted by independent groups such as the Institute of Medicine has found no proven link between breast implants and autoimmune or other systemic diseases.
Other important considerations:
- Breast implants are not guaranteed to last a lifetime and future surgery may be required to replace one or both implants.
- Pregnancy, weight loss and menopause may influence the appearance of augmented breasts over the course of your lifetime.
Many patients have questions about breast augmentation and recovery.
Although many factors are involved with determining your actual recovery time for breast augmentation, you will likely experience a post-surgical recovery period of 24 to 48 hours and an additional reduced-activity period of a few days, you will likely experience soreness and swelling for a few weeks.
Exercise and normal activity can resume at the direction of your plastic surgeon. Over time, post-surgical swelling will decrease and incision lines will fade.
You will be given specific instructions that may include: How to care for your breasts following breast augmentation surgery, medications to apply or take orally to aid healing and reduce the risk of infection, and when to follow-up with your plastic surgeon.
Be sure to ask your plastic surgeon specific questions about what you can expect during your individual recovery period.
- Where will I be taken after my surgery is complete?
- What medication will I be given or prescribed after surgery?
- Will I have dressings/bandages after surgery?
- When will they be removed?
- Are stitches removed? When?
- When can I resume normal activity and exercise?
- When do I return for follow-up care?
When you go home
If you experience shortness of breath, chest pains, or unusual heart beats, seek medical attention immediately. Should any of these complications occur after breast augmentation, you may require hospitalization and additional treatment.
The practice of medicine and surgery is not an exact science. Although good results are expected, there is no guarantee. In some situations, it may not be possible to achieve optimal results with a single surgical procedure and another surgery may be necessary.
Be careful
Following your physician’s instructions is key to the success of your surgery. It is important that the surgical incisions are not subjected to excessive force, abrasion, or motion during the time of healing. Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to care for yourself.
 The results of your breast augmentation surgery will be long-lasting. You will find it easier to wear certain styles of clothing and swim wear. Like many women who have had breast augmentation, you may also have a boost in self confidence.
The results of your breast augmentation surgery will be long-lasting. You will find it easier to wear certain styles of clothing and swim wear. Like many women who have had breast augmentation, you may also have a boost in self confidence.
Implants may need to be replaced or revised
It’s important to know that after receiving breast implants, results are not permanent and they may require replacement during your lifetime. You should expect to have future visits with your plastic surgeon to discuss changes in your breasts.
Over time, your breasts can change due to aging, weight fluctuations, hormonal factors and gravity. If, after a period of years, you become dissatisfied with the appearance of your breasts, you may choose to undergo a breast lift or implant exchange to restore a more youthful contour.
Continue to follow your plastic surgeon’s instructions to ensure the best results for breast enlargement or breast enhancement, and attend follow-up visits as scheduled.
.jpg) As an elective surgery, the cost of breast augmentation is a consideration for many patients. A surgeon’s cost for breast augmentation may vary based on his or her experience, the type and cost of breast implants used, as well as geographic office location.
As an elective surgery, the cost of breast augmentation is a consideration for many patients. A surgeon’s cost for breast augmentation may vary based on his or her experience, the type and cost of breast implants used, as well as geographic office location.
Many plastic surgeons offer patient financing plans, so be sure to ask.
Cost may include:
- Surgeon’s fee
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- Anesthesia fees
- Breast implant cost
- Prescriptions for medication
- Post-surgery garments
- Medical tests
Most health insurance plans will not cover cosmetic breast augmentation costs, related complications or another surgery to revise the appearance of your breasts. Some carriers even exclude breast diseases in patients who have breast implants. You must carefully review your health insurance policy.
Your satisfaction involves more than a fee
When choosing a plastic surgeon for breast enlargement or breast enhancement, remember that the surgeon’s experience with breast implants and your comfort with him or her are just as important as the final cost of the surgery.
- Areola: Pigmented skin surrounding the nipple.
- Augmentation mammaplasty: Breast enlargement or breast enhancement by surgery.
- Breast Augmentation: Also known as augmentation mammaplasty; breast enlargement or breast enhancement by surgery.
- Breast Implants: Medical devices placed in your body to enhance an existing breast size or to reconstruct your breast. Breast implants fall into two categories: saline breast implants and silicone breast implants.
- Capsular contracture: A complication of breast implant surgery which occurs when scar tissue that normally forms around the implant tightens and squeezes the implant and becomes firm.
- General anesthesia: Drugs and/or gases used during an operation to relieve pain and alter consciousness.
- Hematoma: Blood pooling beneath the skin.
- Inframammary incision: An incision made in the fold under the breast.
- Intravenous sedation: Sedatives administered by injection into a vein to help you relax.
- Local anesthesia: A drug injected directly to the site of an incision during an operation to relieve pain.
- Mammogram: An x-ray image of the breast.
- Mastectomy: The removal of breast tissue, typically to rid the body of cancer.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging; a painless test to view tissue similar to an x-ray.
- Periareolar incision: An incision made at the edge of the areola.
- Saline implants: Breast implants filled with salt water.
- Silicone implants: Breast implants filled with an elastic gel.
- Submammary or subglandular placement: Breast implants placed directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle.
- Submuscular or subpectoral placement: Breast implants placed under the pectoral muscle, which is located between the breast tissue and chest wall.
- Sutures: Stitches used by surgeons to hold skin and tissue together.
- Transaxillary incision: An incision made in the underarm area.
- Ultrasound: A diagnostic procedure that projects high frequency sound waves into the body and records the echoes as pictures.
It is important to be an active participant in the process, so we’ve developed the following list of questions to ask about breast augmentation during your consultation:
- Are you certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery?
- Were you trained specifically in the field of plastic surgery?
- How many years of plastic surgery training have you had?
- Do you have hospital privileges to perform this procedure?
- If so, at which hospitals?
- Is the office-based surgical facility accredited by a nationally-or state-recognized accrediting agency, or is it state-licensed or Medicare-certified?
- Am I a good candidate for breast enhancement or breast enlargement?
- What will be expected of me to get the best results?
- Where and how will you perform my breast augmentation surgery?
- What shape, size, surface texturing, incision site and placement site are recommended for me?
- How long of a recovery period can I expect, and what kind of help will I need during my recovery?
- What are the risks and complications associated with my procedure?
- How are complications handled?
- How many additional implant-related operations can I expect over my lifetime?
- How will my ability to breastfeed be affected?
- How can I expect my implanted breasts to look over time?
- After pregnancy? After breastfeeding?
- What are my options if I am dissatisfied with the cosmetic outcome of my implanted breasts?
- How will my breasts look if I choose to have the implants removed in the future without replacement?
- Do you have breast augmentation before-and-after photos I can look at for this procedure and what results are reasonable for me?
Plastic surgery involves many choices. The first and most important is selecting a surgeon you can trust.
Choosing an ASPS Member Surgeon ensures that you have selected a physician who:
- Has completed at least five years of surgical training with a minimum of two years in plastic surgery.
- Is trained and experienced in all plastic surgery procedures, including breast, body, face and reconstruction.
- Operates only in accredited medical facilities
- Adheres to a strict code of ethics.
- Fulfills continuing medical education requirements, including standards and innovations in patient safety.
- Is board certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or in Canada by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada®.
ASPS Member Surgeons are your partners in cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery.
Look for the ASPS Member Surgeon logo.

 3510 N. Ridge Rd, Suite 100
3510 N. Ridge Rd, Suite 100